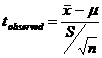The z and t Statistic
One of the most basic hypothesis tests is a test about a population mean. A researcher might be interested in testing to determine whether an established or accepted mean value for an industry is still true or in testing a hypothesized mean value for a new theory or product.
The following z-test formula can be used to test hypotheses about a single population mean when σ is known and sample size n ≥ 30 and x is known to be normally distributed.
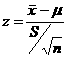
If n < 30 or x is not normally distributed:
|
|
|
If making a claim against one population proportion (p), if n < 30 and x is normally distributed:
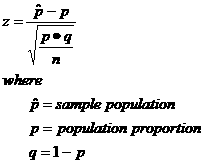
If n < 30 or x is not normally distributed:
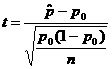
Hypotheses Testing for two means.
If n1 > 30, n2 > 30 and x is normally distributed:
H0: µ1 = µ2
Ha: µ1 ≠ µ2
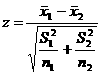
If n1 < 30, n2 < 30 and x is not normally distributed:
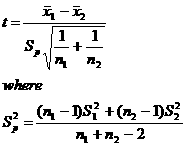
Hypotheses testing for two proportions (p1, p2)
If n1 > 30, n2 > 30 and x is normally distributed:
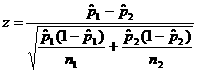
If n1 < 30, n2 < 30 and x is not normally distributed:
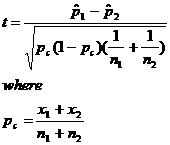
Suggested Readings
- Statistics Glossary
http://www.stats.gla.ac.uk/steps/glossary/hypothesis_testing.html - Elon University Statistics Page
http://math.elon.edu/statistics112/index.html - Online Stats Book
http://onlinestatbook.com/ - Statistics Explained
http://www.animatedsoftware.com/ascodesc/statdesc.htm - Data, Probability and Statistics
http://www.mathsisfun.com/probability/index.html